Bear Put Spread – Moderately Bearish Option Strategy

A defined-risk bearish strategy created by buying a higher strike Put and selling a lower strike Put, suitable for moderately bearish outlooks.
Bear Put Spread: The Defined-Risk, Moderately Bearish Strategy
A Bear Put Spread is a calibrated, debit-based options strategy employed when a trader holds a moderately bearish outlook on an underlying asset. It is constructed by purchasing one put option at a higher strike price and simultaneously selling another put option at a lower strike price, both with the same expiration date. This vertical spread approach significantly reduces the net cost of establishing a bearish position compared to a naked long put, while simultaneously defining and limiting both the maximum potential profit and loss.
The core appeal of the Bear Put Spread lies in its cost-efficiency and risk-managed profile. It is specifically designed to profit from a measured downward move within a predetermined price range. By selling the lower-strike put, the trader sacrifices the unlimited profit potential of a catastrophic crash in exchange for a lower entry cost and a higher probability of achieving a profitable outcome on a more modest decline.
- Risk is Precisely Defined: The maximum loss is strictly limited to the net debit (premium paid) to enter the spread. This is known upfront and cannot be exceeded.
- Profit is Capped but Favorable: Maximum profit is achieved if the underlying closes at or below the lower (sold) strike price at expiration. It is calculated as (Width of Spread - Net Debit).
- Cost-Effective Bearish Exposure: The premium received from selling the lower-strike put directly subsidizes the cost of buying the higher-strike put, resulting in a lower net investment and lower breakeven point.
When to Deploy a Bear Put Spread
This strategy is strategically optimal when your analysis suggests a controlled, downward price movement rather than a panic-driven collapse. It balances cost, risk, and probability effectively.
- When technical indicators suggest a breakdown from a key support level or a pullback within a larger uptrend.
- When a stock or index is facing resistance, shows bearish divergence on oscillators like the RSI, or is in a overbought condition.
- Before an event expected to cause modest negative pressure (e.g., a slightly disappointing earnings report, a downgrade).
- When implied volatility is moderate or high, making outright long puts expensive. The spread helps mitigate this cost.
- When you want bearish exposure but are also conscious of capital preservation and defined risk.
Strategic Setup Checklist
- Underlying Asset: Choose liquid stocks or indices with active options markets (e.g., NIFTY, Bank NIFTY, Reliance, Infosys) to ensure tight bid-ask spreads.
- Strike Selection: Typically, buy an At-The-Money (ATM) or slightly In-The-Money (ITM) put and sell a further Out-of-The-Money (OTM) put. The distance between strikes defines your risk-reward ratio.
- Expiry Cycle: Ideal timeframes are 3-6 weeks to expiration. This provides sufficient time for the anticipated move to materialize while managing the negative effects of time decay.
- Cost Analysis: Calculate the net debit carefully. Ensure the potential reward (spread width - debit) justifies the risk (debit) and aligns with your outlook for the size of the downward move.
Step-by-Step Entry Rules
- Buy 1 Put Option at a higher strike price (e.g., ATM or ITM). This is your primary bearish bet.
- Sell 1 Put Option at a lower strike price (OTM). This financees your long put and defines your maximum profit.
- All options must share the same underlying and expiration date.
- Net Debit = (Premium of Long Put) - (Premium from Short Put). This is your total cost and maximum loss. Pay this amount to enter the trade.
Risk & Position Management Profile
The Bear Put Spread offers a clear and manageable risk profile, making it suitable for disciplined traders.
- Maximum Loss: Limited to the net debit paid. This occurs if the underlying price is at or above the higher (long) strike price at expiration. All options expire worthless or the loss on the long put is exactly offset by the premium collected from the short put.
- Maximum Profit: Limited and achieved if the underlying price is at or below the lower (short) strike price at expiration. Calculated as: (Higher Strike - Lower Strike - Net Debit) * Lot Size.
- Theta (Time Decay): The effect is mixed but generally negative. The long put suffers from time decay, while the short put benefits from it. The net effect is that the position will lose value over time if the price remains static, though at a slower rate than a naked long put.
- Vega (Volatility Risk): The position is generally long vega. An increase in implied volatility (IV) after entry will increase the value of the spread (helpful), while a decrease in IV will hurt the position. This is because the long put has higher vega than the short put.
- Adjustments: If the market moves against you (rises), the loss is capped. If it moves favorably but you anticipate a further drop, you could potentially "roll" the entire spread down to lower strikes for a additional debit.
Exit Rules and Trade Management
- Profit Taking: If the underlying price falls near your lower strike target before expiration, consider closing the position early to lock in a majority of the potential profit. This avoids the risk of the price bouncing back before expiry.
- Stop-Loss (Technical or Monetary): If the underlying price breaks above a key resistance level, invalidating your bearish thesis, exit the trade early even for a loss smaller than the max loss. Alternatively, set a monetary stop-loss (e.g., 50% of the net debit).
- Expiration: Manage the position actively at expiration. If the price is between your strikes, you may be assigned on the short put. Be prepared to either take delivery of shares or close the spread before the market closes.
Position Sizing & Prudent Money Management
- The maximum loss (net debit) for any single Bear Put Spread should be a small fraction of your total trading capital (e.g., 1-2%).
- Do not overleverage by using too much buying power on multiple spread positions simply because the risk is "defined."
- Use this strategy as part of a diversified approach, not as your sole bearish tool.
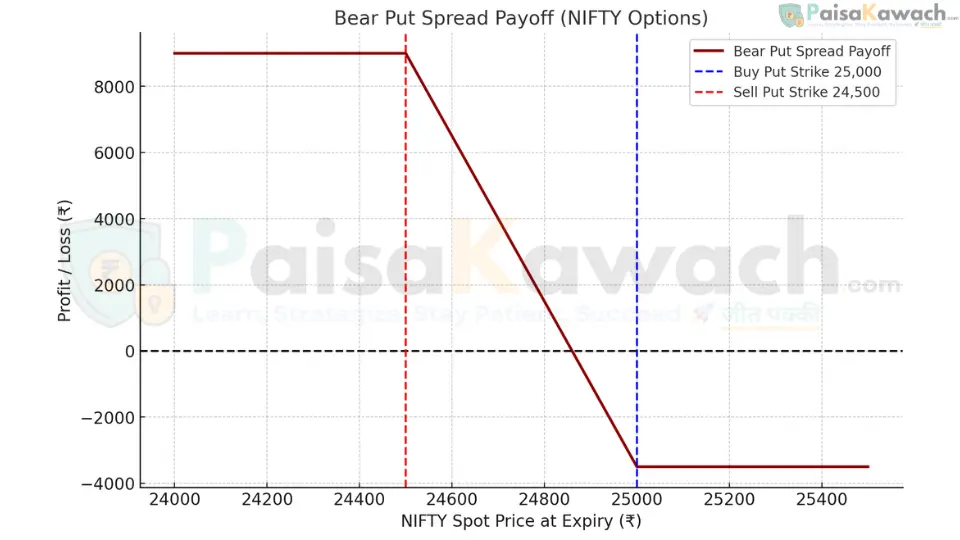
Detailed Example: NIFTY Bear Put Spread
Assume NIFTY is trading at ₹25,000. You anticipate a pullback to the ₹24,600 level over the next month.
- Buy 1 NIFTY 25,000 PE (Put) at a premium of ₹260
- Sell 1 NIFTY 24,500 PE (Put) at a premium of ₹120
Net Debit (per share): ₹260 - ₹120 = ₹140
Lot Size: 75 units (Standard for NIFTY options)
Total Capital at Risk (Max Loss): ₹140 * 75 = ₹10,500 (approx. $126)
Maximum Profit Calculation:
Spread Width = 25,000 - 24,500 = 500 points.
Max Profit (per share) = (500 - 140) = ₹360
Total Maximum Profit: ₹360 * 75 = ₹27,000 (approx. $324)
Breakeven Point Calculation:
Breakeven at Expiry: Higher Strike - Net Debit = 25,000 - 140 = ₹24,860
NIFTY must close at or below ₹24,860 at expiration for the trade to be profitable. The trade achieves maximum profit if NIFTY closes at or below ₹24,500.
Payoff Scenarios at Expiry:
- Scenario 1 (Max Profit - Sharp Decline): NIFTY expires at 24,400.
The long 25,000 put is ITM by ₹600. The short 24,500 put is ITM by ₹100 and must be bought back.
Net Profit = ₹600 (from long put) - ₹100 (loss on short put) - ₹140 (net debit) = ₹360 per share.
Total Profit = ₹27,000
Alternatively, the spread is worth its maximum value of ₹500. You paid ₹140, so your profit is ₹360. - Scenario 2 (Max Loss - Rally or Stagnation): NIFTY expires at 25,100 (or above).
Both puts expire worthless.
Total Loss = ₹10,500 (the initial net debit paid) - Scenario 3 (Small Profit - Moderate Decline): NIFTY expires at 24,900.
The long 25,000 put is ITM by ₹100. The short 24,500 put expires worthless.
Net Profit = ₹100 (from long put) - ₹140 (net debit) = -₹40 per share (Loss)
Total Loss = ₹3,000
This shows that the trade is only profitable if NIFTY falls below the breakeven point of ₹24,860.
Key Metrics and Greeks to Monitor
- Breakeven Point: The critical price level that must be breached for profitability.
- Delta: Negative, indicating a bearish position. The value becomes more negative as the price falls and approaches zero as the price rises.
- Gamma: Highest when the price is near the strikes, affecting how quickly delta changes.
- Theta: Generally negative, but the short put helps mitigate the time decay compared to a naked long put.
- Vega: Positive. The position benefits from an increase in implied volatility.
Advantages of a Bear Put Spread
- Significantly lower cost and lower breakeven point than a naked long put.
- Clearly defined and limited maximum risk.
- Higher probability of profit compared to a naked long put for a given downward move, due to the cheaper cost.
- Effective for capitalizing on moderate, expected declines.
- Requires less of a price move to become profitable compared to a vertical spread initiated with OTM options.
Disadvantages of a Bear Put Spread
- Profit potential is capped at the lower strike. A massive crash beyond the short put strike does not yield additional profits.
- Still susceptible to time decay, though less than a naked long put.
- Requires more precise forecasting than a simple long put; the price must decline enough to overcome the net debit but not so much that you regret the capped upside.
Strategic Comparison: Bear Put Spread vs. Long Put
| Factor | Bear Put Spread | Long Put (Naked) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower (Net Debit) | Higher (Full Premium) |
| Breakeven Point | Higher (Closer to current price) | Lower (Further from current price) |
| Maximum Risk | Limited (Net Debit) | Limited (Premium Paid) |
| Maximum Reward | Capped (Spread Width - Debit) | Very Large (Theoretical) |
| Ideal Market Outlook | Moderately Bearish | Very Bearish / Crash |
The Bear Put Spread is a strategic and risk-conscious tool for traders who have a measured bearish conviction. It exemplifies the trade-off in options trading: sacrificing unlimited profit potential for a cheaper, higher-probability trade with strictly managed risk. It is an essential strategy for any options trader looking to express a bearish view without overpaying for insurance.
